By Yong-Suk Kim1, Hyungjoon Jun1, Younbyoung Chae2, Hi-Joon Park3, Bong Hyun Kim4, Il-Moo Chang4, Sung-keel Kang5 and Hye-Jung Lee2
- 1Department of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, College of Oriental Medicine, Kangnam Korean Hospital,
- 2Department of Oriental Medical Science, Graduate School of East-West Medical Science,
- 3Department of Meridian and Acupuncture, College of Korean Medicine, Kyung Hee University,
- 4Natural Products Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul, South Korea
- 5Department of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, College of Oriental Medicine, Kyung Hee University, South Korea
Acupuncture for Stroke
Stroke
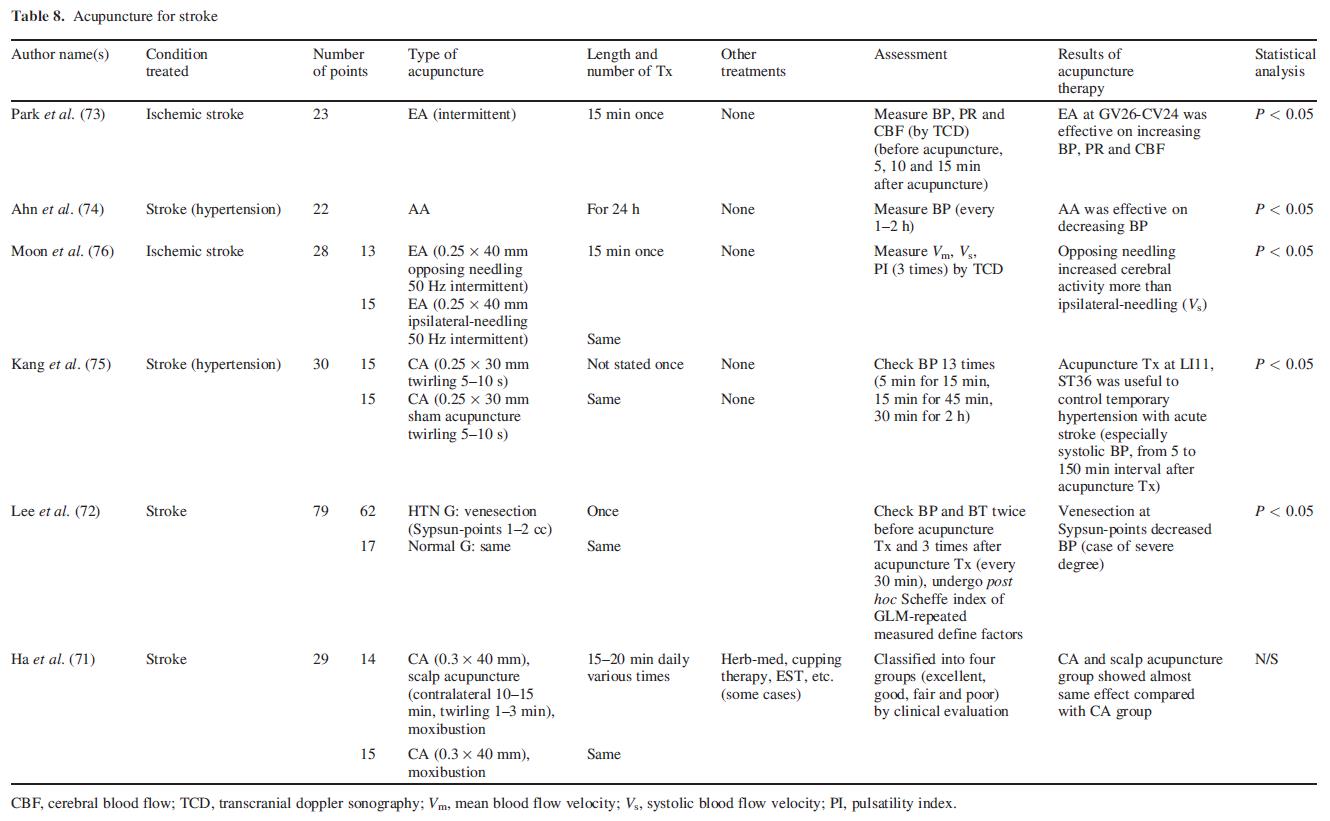
Ha et al. (71) reported a clinical study of acupuncture and scalp acupuncture on stroke patients (29 cases). Lee et al. (72) evaluated the change of blood pressure and body temperature of the stroke patients after venesection at Sybsun points, 10 acupoints located at the tips of all fingers and demonstrated that venesection at Sybsun points could alleviate hypertension in stroke patients. Park et al. (73) examined electrical stimulation at GV26 and CV24 on blood pressure, heart rate and cerebral blood flow (CBF) in ischemic stroke patients with transcranial doppler sonography. Ahn et al. (74) investigated change in 24 h blood pressure after auricular acupuncture treatment in stroke patients using an ambulatory blood pressure monitor. Kang et al. (75) compared acupuncture at ST36 and LI11 with stimulation at non-acupoints near these acupoints for the modulation of hypertension of acute stroke patients. Moon et al. (76) compared acupuncture at ipsilateral points with that at contralateral points on the cerebral blood flow (CBF) in ischemic stroke patients (Table 8).
Poststroke Diseases
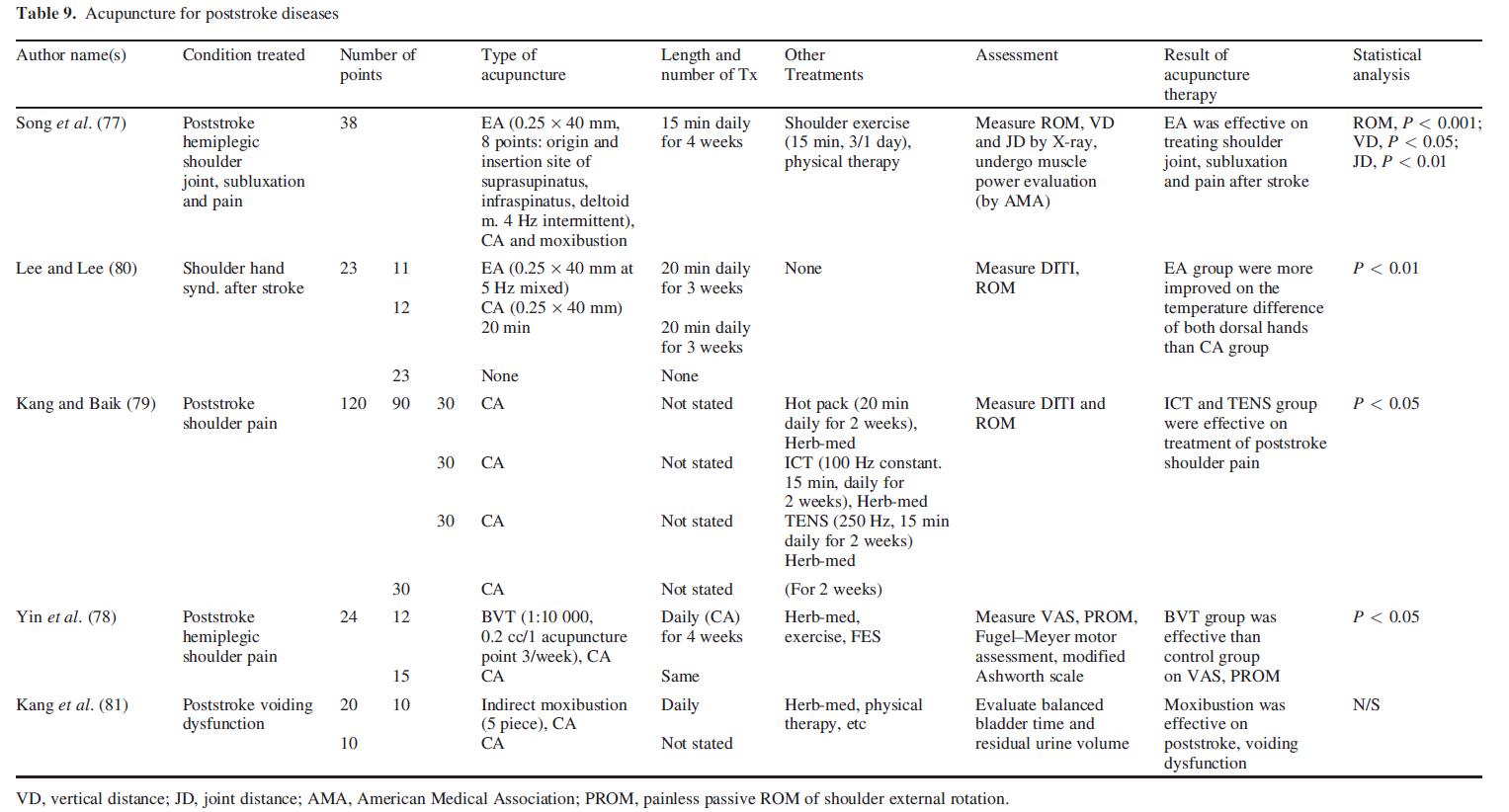
Electric acupuncture could alleviate shoulder pain in cerebrovascular attack patients (77). It was demonstrated that BVA at LI15 and SI10 decreased visual analog scale of pain severity and increased painless passive range of motion of shoulder eternal rotation in hemiplegic shoulder pain patients (78). Kang and Baik (79) compared the therapeutic value of transcutanous electrical nerve stimulation with interferential current therapy, infrared or hot pack treatments for shoulder pain in cerebrovascular attack patients. Lee and Lee (80) evaluated the effect of acupuncture and electric acupuncture on shoulder hand syndrome by using DITI. Kang et al. (81) examined the balanced bladder time and residual urine volume and demonstrated the clinical efficacy of moxibustion at CV3, CV4 and CV6 in patients with voiding dysfunction after a cerebrovascular accident (Table 9).
Acupuncture for Facial Palsy
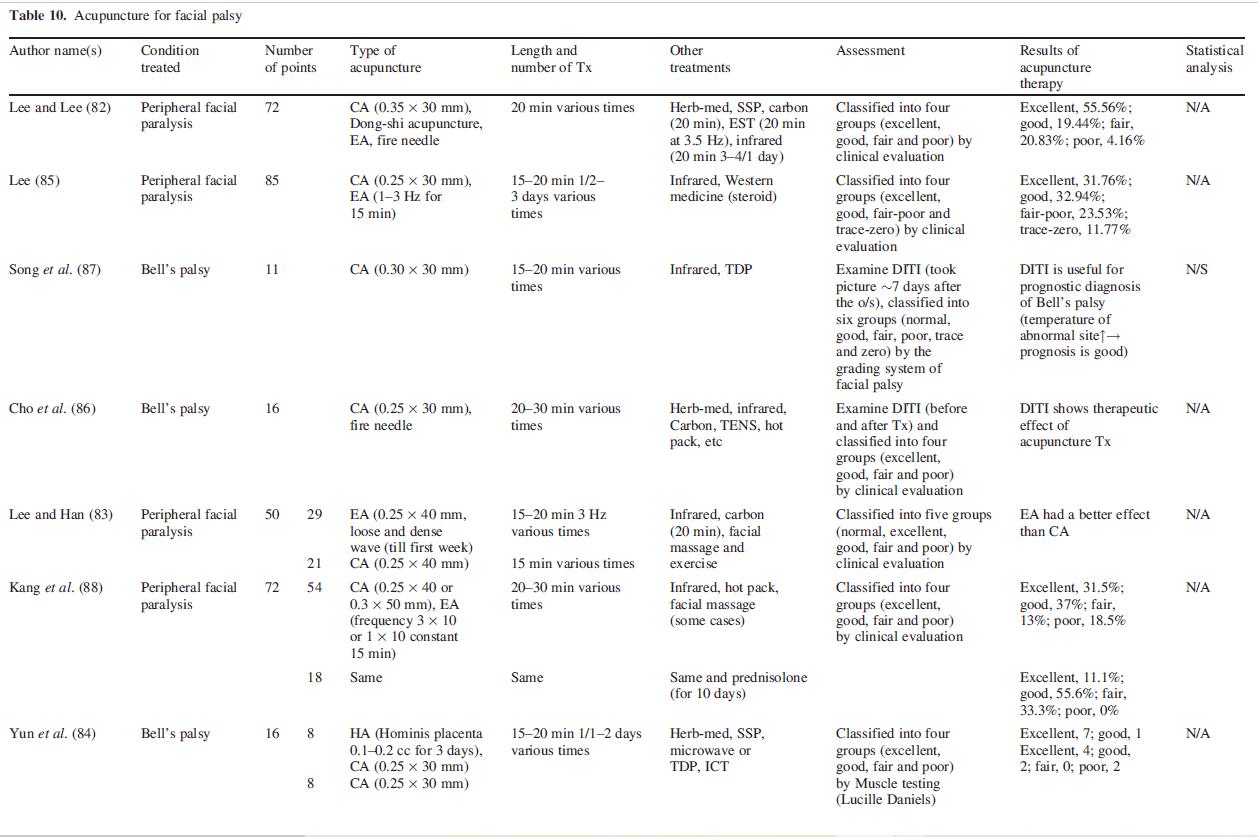
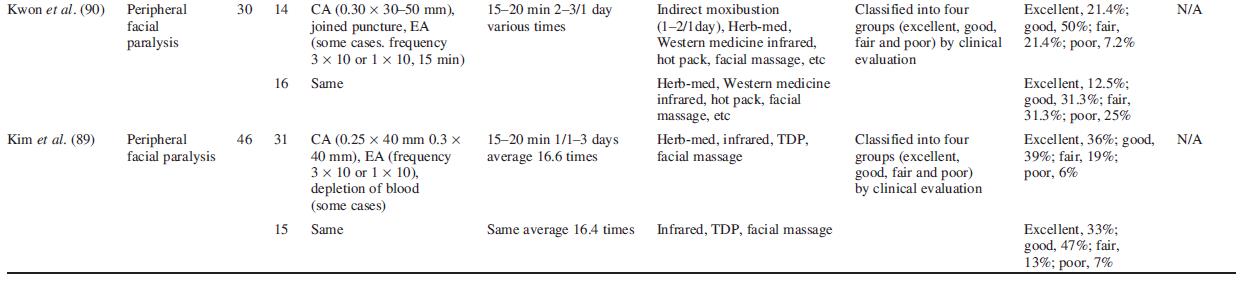
Acupuncture treatment was beneficial in 72 cases of patients with facial paralysis (82). Moreover, electric acupuncture was better than needling in the treatment of patients with peripheral facial nerve paralysis (83). The effect of Hominis placenta acupuncture, a kind of HA, on Bell’s palsy was reported (84). It was demonstrated that Saam acupuncture at liver and stomach tonification points could treat peripheral facial palsy (85). Cho et al. observed the change of clinical symptoms and DITI, showing the benefits of acupuncture and herbal medicine in patients with Bell’s palsy (86,87).
Kang et al. compared a group treated by Oriental-Western treatment with a group treated by Oriental medical therapy by evaluating House–Brackmeann grading system and made a detailed evaluation of facial symmetry of Pillsbury and Fisch (88,89). Kim et al. (89) compared a group treated by both acupuncture and herbal medicine with a group treated by acupuncture in patients of facial nerve paralysis and demonstrated that the symptoms were improved in both groups. Kwon et al. (90) compared a group treated by conventional Oriental medicine therapy with a group treated by conventional Oriental medicine therapy and indirect moxibustion at ST4 and ST8 in peripheral facial paralysis patients (Table 10).
Acupuncture for Other Conditions
Eye Disease (Opthalopathy)
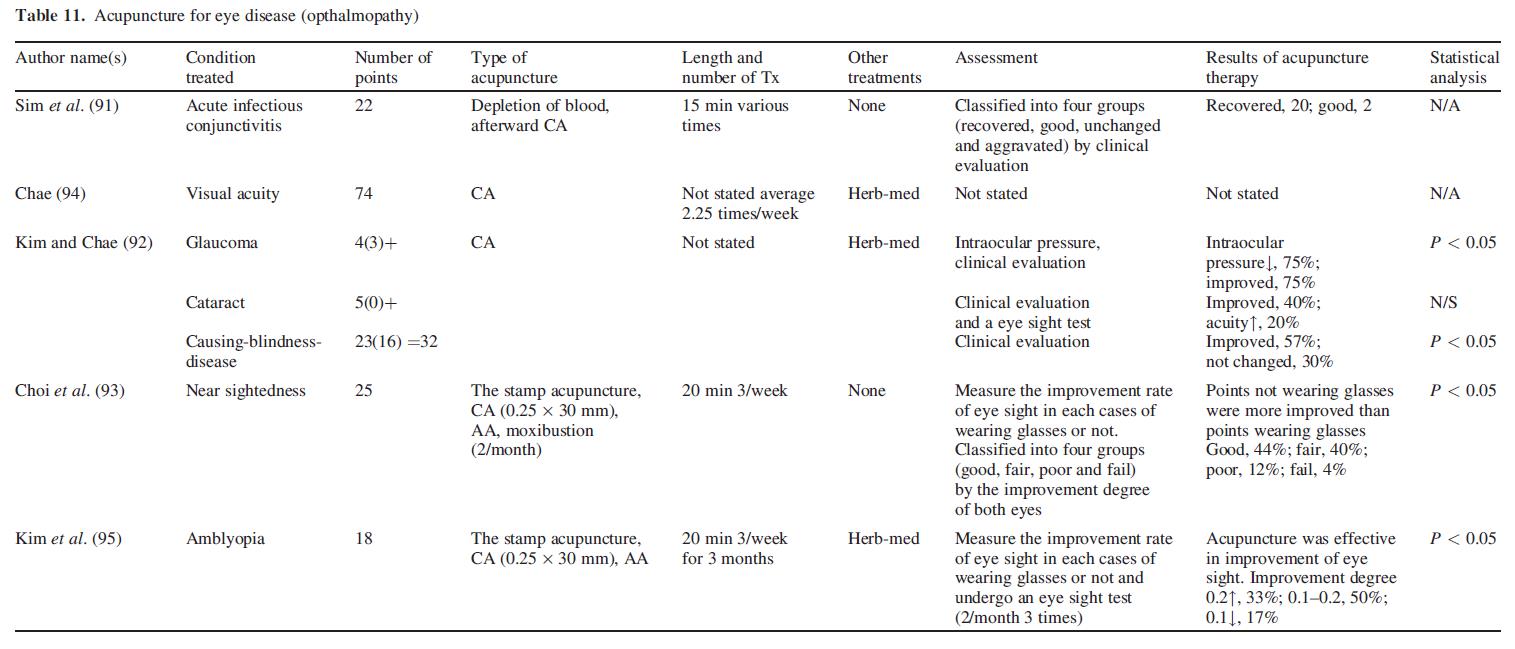
Acupuncture and venesection were useful in treating 22 patients who suffered from acute infectious conjunctivitis (91). Kim and Chae (92) reported 32 patients with cataract or glaucoma who were treated by Oriental medicine and acupuncture. The therapeutic effect of acupuncture and moxibustion on the sight of near-sighted patients was also reported (93,94). Clinical studies were carried out to demonstrate the effect of Oriental medicine and acupuncture on amblyopia (95) (Table 11).
Nose Disease (Rhinopathy)
Acupuncture was effective in the treatment of allergic rhinitis in 30 patients (96). Nasal acupuncture therapy was investigated
to treat the chronic paranasal sinusitis and nasal obstruction (97,98) (Table 12).
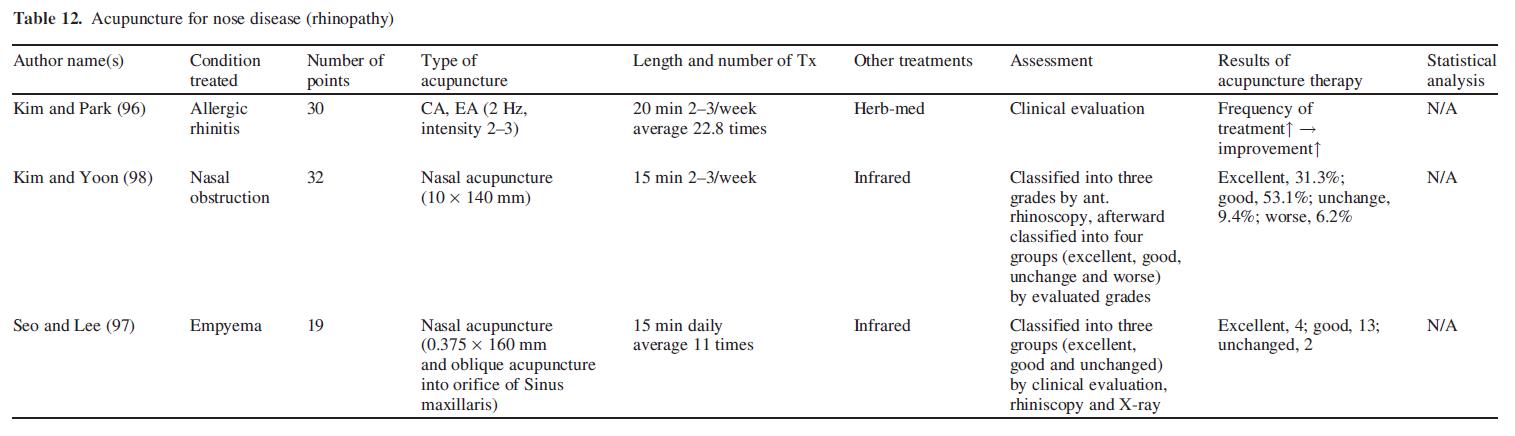
Ear Disease (Otopathy)
Clinical studies were carried out to investigate acupuncture, moxibustion and venesection for tinnitus (99,100). It was reported that acupuncture at TE5, GI41, TE6 SI5, GI38, KI2 and venesection improved symptoms of patients with otitis media with effusion (101) (Table 13).
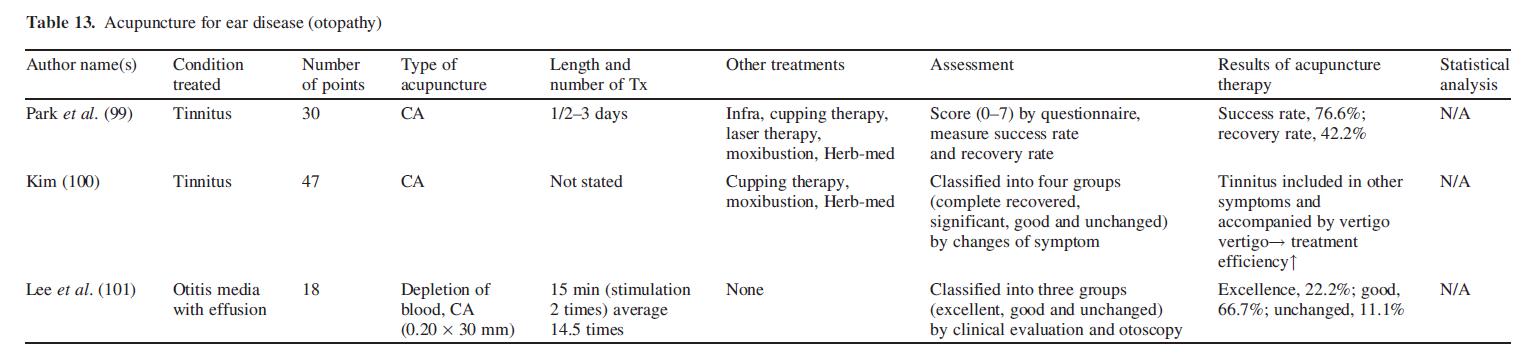
Skin Disease (Dermatology)
It was reported that acupuncture and herbal medicine were effective in the treatment of acne in 125 patients (102). It was also found that acupuncture and herbal medicine improved the symptoms of the acne patients (103) (Table 14).
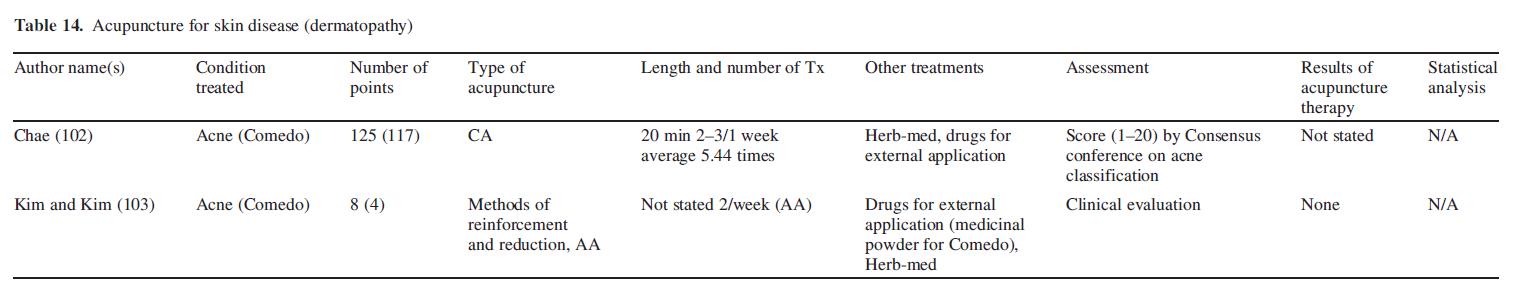
Hypertension
Clinical studies with auricular acupuncture were performed on 23 patients with hypertension (104). Lee et al. (105) examined
moxibustion at LI11 and CV4 for blood pressure of hypertension patients (Table 15).
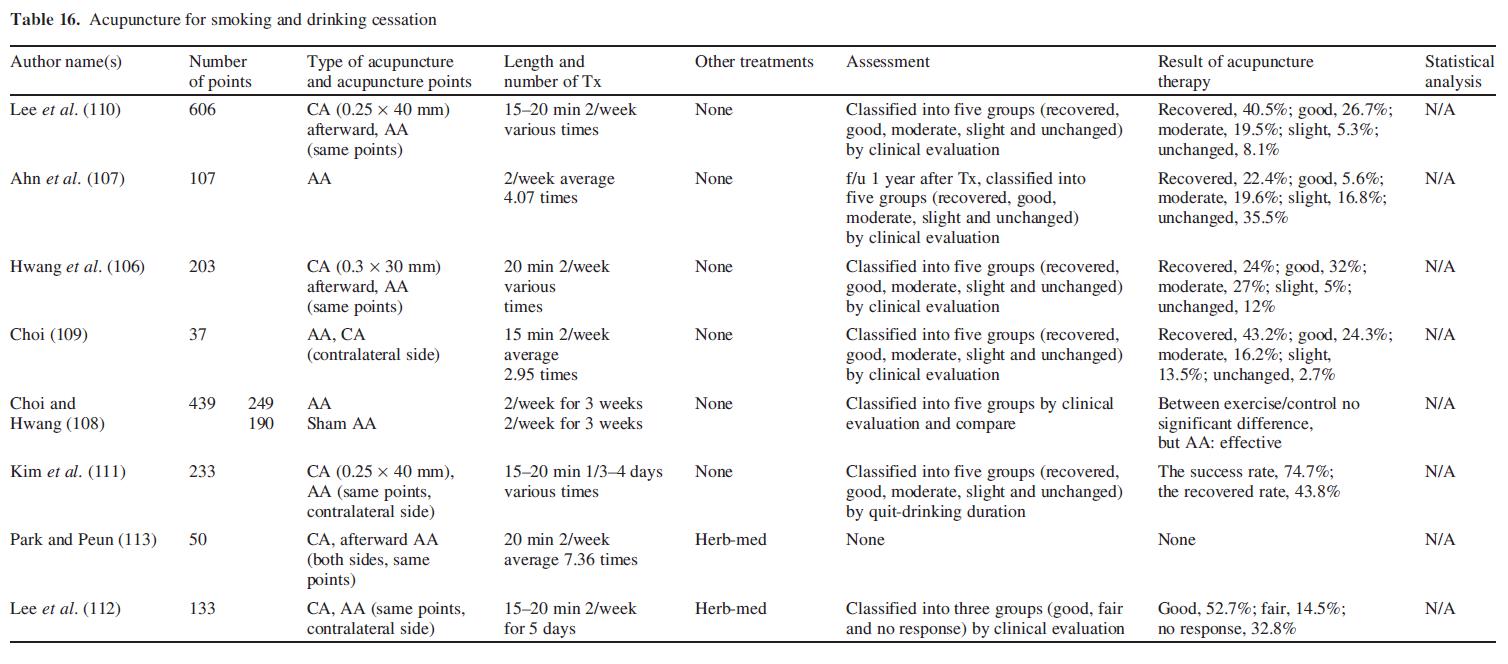
Smoking and Drinking Cessation
Auricular acupuncture to stop smoking (106–110). Kim et al. investigated the effect of auricular acupuncture on cessation
of drinking in alcoholic patients (111,112). It was reported that auricular acupuncture and herbal medicine were effective
for quitting drinking (113) (Table 16).
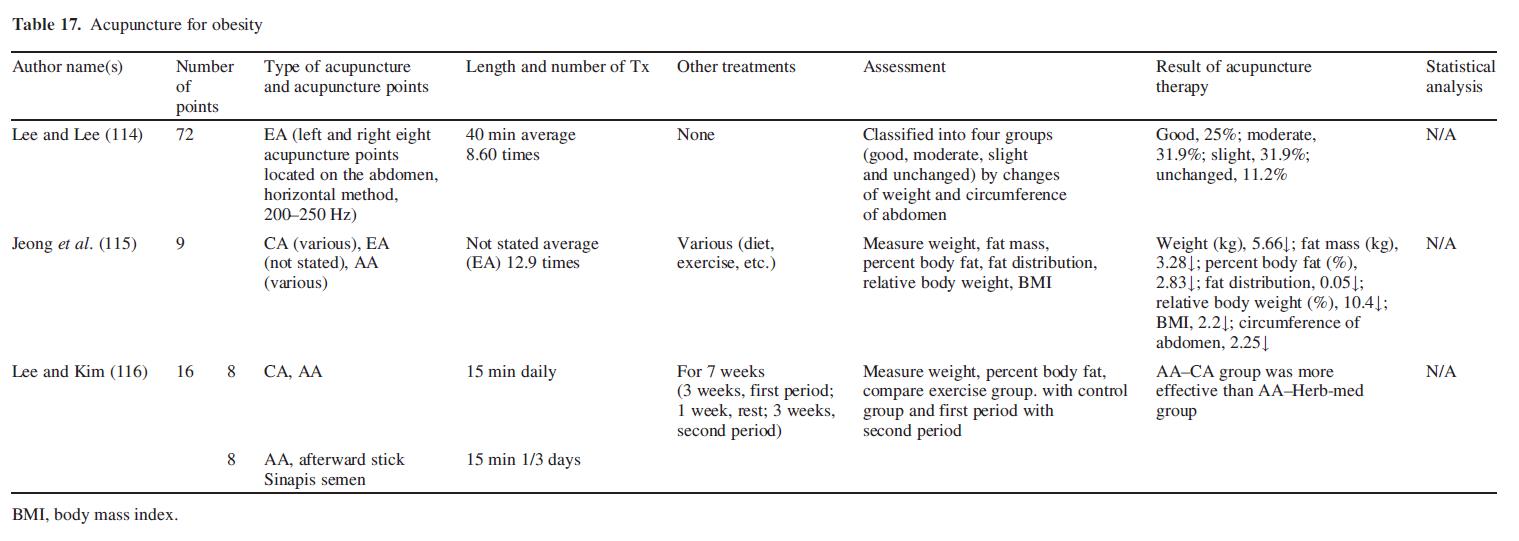
Obesity
Electric acupuncture decreased body weight, abdominal length, size of waist and body mass index (114,115). Lee and Kim (116) compared auricular acupuncture combined with acupuncture with auricular acupuncture combined with herbal medicine for the treating obesity by measuring body weight and percentage of body fat (Table 17).
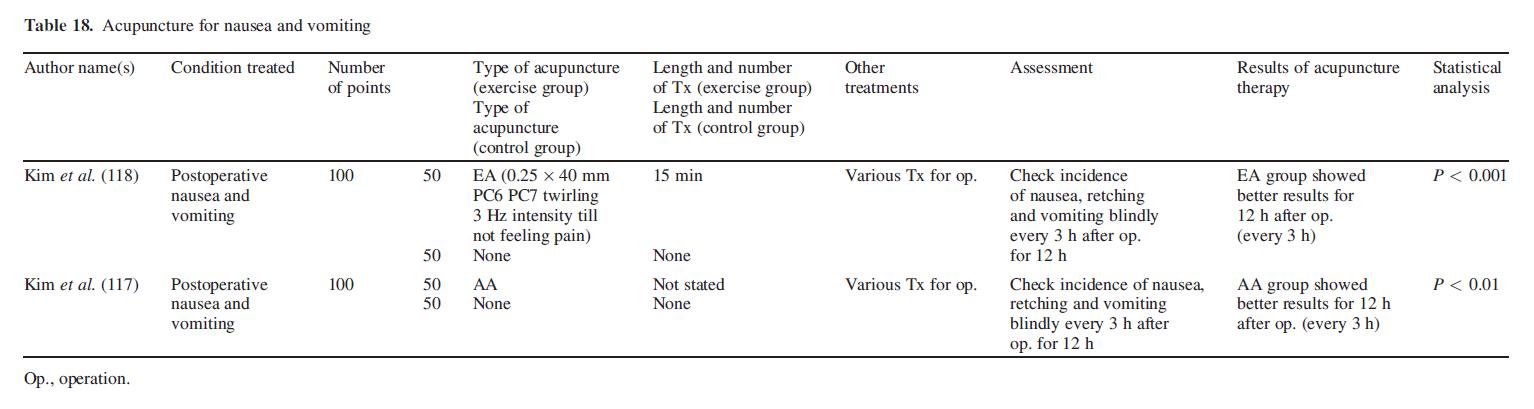
Nausea and Vomiting
Auricular acupuncture on sympathetic, stomach, shenmen and occiput points for postoperative nausea and vomiting in 100 female patients undergoing transabdominal hysterectomy. It was demonstrated that electric acupuncture at PC6 and PC7 was very effective in preventing nausea, retching and vomiting (118) (Table 18).
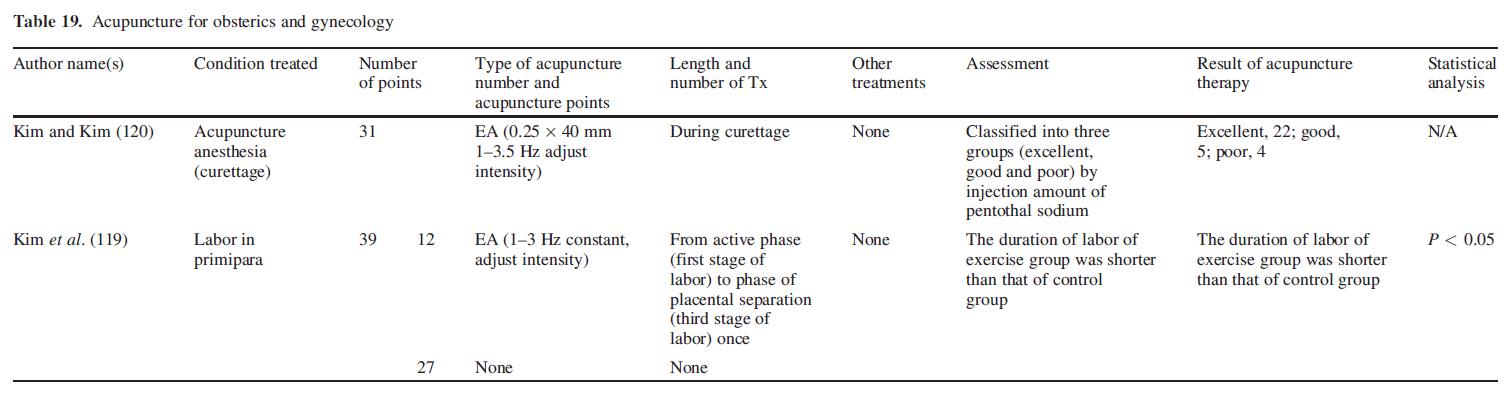
Obstetrics and Gynecology
Electric stimulation at acupuncture points significantly shortened the delivery time and attenuated the pain during delivery (119). Moreover, endometrial curettage was successfully performed on 31 female patients under acupuncture anesthesia (120) (Table 19).
Others
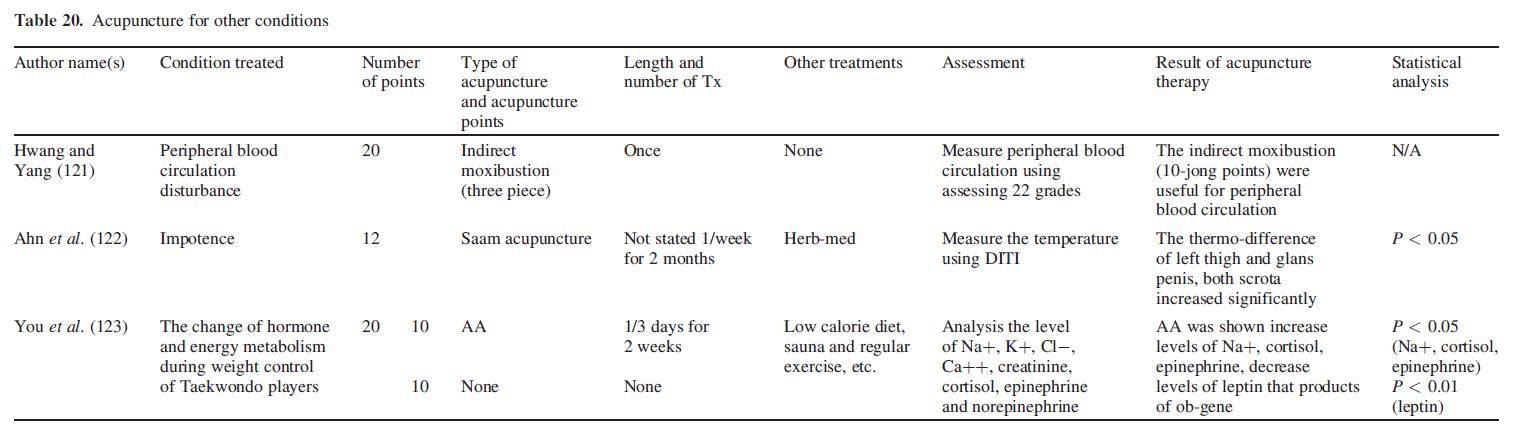
Moxibustion could have an effect on peripheral circulation (121). Ahn et al. (122) examined the temperature change of external genitalia in patients with impotence after herbal medicine and acupuncture treatment. Auricular acupuncture altered hormone and energy metabolism during weight control of athletes (123) (Table 20).
References
71. Ha CH, Han SG, Cho MR, Ryu CR, Lee BR. A clinical study on 29 cases with stroke treated by common acupuncture therapy and scalp acupuncture. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 2001;18:82–90.
72. Lee KJ, Koo BS, Kim YS, Kang JK, Moon SK, Koh CN, et al. Effects of venesection at the Sybsun-points on blood pressure and body temperature in patients with stroke. J Kor Oriental Med Soc 2000;21:62–7.
73. Park SU, Moon SK, Koh CN, Cho KH, Kim YS, Bae HS, et al. The clinical study of the effect of electrical stimulation at Sugu-Sungjang points (GV26-CV24) on blood pressure, pulse, and cerebral blood flow in ischemic stroke patients. Kyunghee Med 1997;13:390–403.
74. Ahn CH, Bae HS, Roh JH, Moon SK, Koh CN, Cho KH, et al. Effects of auricular acupuncture on the mild hypertension. J Kor Oriental Med Soc 2000;20:93–7.
75. Kang BJ, Moon SK, Koh CN, Cho KH, Kim YS, Bae HS, et al. Clinical research on the depressing effect of acupuncture therapy at Kokchi (LI11) and Chocksamni (ST36) in acute stroke patients with hypertension. J Oriental Med 1998;3:43–50.
76. Moon SK, Cho KH, Koh CN, Kim YS, Bae HS, Lee KS. Effects of opposing needling on upper limb on cerebral blood flow in ischemic stroke patients. Kyunghee Med 2000;16:94–101.
77. Song JC, Jung SH, Lee JS, Kim SS, Shin HD. Clinical study of the effect of electroacupuncture on shoulder pain of the cerebrovascular attack patients. J Oriental Rehabil Med 1999;9:41–57.
78. Yin CS, Nam SS, Kim YS, Lee JD, Kim CH, Koh HK. Effects of honey bee venom acupuncture therapy on poststroke hemiplegic shoulder pain. J Kor Inst Herbal Acu 2000;3:213–32.
79. Kang JC, Baik TH. A comparative study of effects using physical treatment apparatus and diagnosis of shoulder pain on cerebrovascular attack patients. Kor Int Med Soc 1999;20:244–60.
80. Lee SH, Lee YH. Clinical study with thermography on shoulder hand syndrome after stroke. J Kor Oriental Med Soc 1997;18:25–39.
81. Kang KS, Jeong EJ, Moon SK, Koh CN, Cho KH, Kim YS, et al. Clinical study on the effects of moxibustion for post-stroke voiding dysfunction. J Kor Oriental Med Soc 2000;21:236–41.
82. Lee YK, Lee BR. Clinical studies on 72 cases of patient with facial paralysis. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 1998;15:1–12.
83. Lee SW, Han SW. Clinical study of facial nerve paralysis through electroacupuncture treatment. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 1999;16: 149–63.
84. Yun JH, Yook TH, Song BY. The effect of Hominis placenta herbal acupuncture. J Kor Inst Herbal Acu 2000;3:89–99.
85. Lee KM. Combined treatment method for peripheral facial paralysis: report on 85 cases. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 1998;15:21–9.
86. Cho EH, Cho NG, Hur TY, Cheon MN. Clinical evaluation of acupuncture and herb medication on Bell’s palsy by DITI. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 2000;17:19–30.
87. Song BY, Sohn IC, Kim KS. Clinical diagnostic study on prognosis of Bell’s palsy with the digital infrared thermal image. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 1999;16:13–35. 88. Kang MJ, Kim KH, Hwang HS. Comparative clinical study between oriental medicine and oritental western medicine treatment on facial nerve paralysis. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 2000;17:55–66.
89. Kim CG, Park SD, Kim KH. Comparative study between acupuncture and acupuncture-oriental herb medicine treatment on facial nerve paralysis. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 2001;18:10–22.
90. Kwon SJ, Song HS, Kim KH. The influence of moxibustion and basic compound therapy on peripheral facial paralysis. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 2000;17:160–71.
91. Sim MK, Hwang WJ, Lim KS. Clinical study of acupuncture and venesection on acute infectious conjunctivitis. J Kor Oriental Med Soc 1993;14:133–8.
92. Kim KJ, Chae BY. A clinical analysis on glaucoma, cataract and causing blindness by oriental medical therapy. J Oriental Med Surg Ophthalmol Otolaryngol 1997;10:340–8.
93. Choi DY, Kim JK, Kim SS. A clinical study of the effect of acupuncture and moxibustion treatment for the near-sightedness. Kor. J Oriental Med Pathol 1999;13:119–23.
94. Chae BY. The clinical study on decrease of visual acuity. J Oriental Med 1997;2:93–108.
95. Kim SS, Kim JK, Choi DY. A clinical study of the effect of oriental medicine and acupuncture treatment for the amblyopia. J Kor Oriental Med Soc 2000;20:23–8.
96. Kim SI, Park DI. A clinical study on allergic rhinitis. Kor Int Med Soc 1998;19:353–63.
97. Seo JC, Lee JD. Clinical study on chronic paranasal sinitis by nasal acupuncture. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 2000;17:99–105.
98. Kim YB, Yoon SH. A clinical observation of the nasal acupuncture therapy on nasal obstruction. J Oriental Med Surg Ophthalmol Otolaryngol 1999;12:205–11.
99. Park GH, Han YM, Ahn SH, Hwang CH. Effect of tinnitus after bleeding, acupuncture, moxa, and laser treatment. J Oriental Med Surg Ophthalmol Otolaryngol 1999;12:396–407.
100. Kim GJ. A clinical analysis on the treatment efficiency of tinnitus by types of bianzheng. J Oriental Med Surg Ophthalmol Otolaryngol 1999;12:182–8.
101. Lee HB, Oh SJ, Kim SK. Clinical study on otitis media with effusion by acupucnture. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 2001;18:92–8.
102. Chae BY. The clinical study of acne patients. J Oriental Med Surg Ophthalmol Otolaryngol 1998;11:251–68.
103. Kim JS, Kim GJ. The clinical observation of 8 cases of acnes diseases. J Oriental Med Surg Ophthalmol Otolaryngol 2001;14:66–75.
104. Byun JY, Ahn SG. Effects of the auricular acupuncture on the blood pressure. J Kor Oriental Med Soc 1996;17:418–26.
105. Lee BH, Kim CH, Seo JC, Youn HM, Jang KJ, Song CH, et al. The effects of moxibustion on blood pressure of hypertentsion patients. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 2001;18:70–6.
106. Hwang BT, Hwang WJ, Shin SY. Clinical research of the acupuncture therapy on stop-smoking. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 1994;11:265–74.
107. Ahn SG, Kim SC, Lee MH, Kim KS. A clinical research of the auricular acupuncture therapy. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 1993;10:175–90.
108. Choi SC, Hwang CY. Effects on stop of smoking in adolescents by auricular acupuncture therapy. J Oriental Med Surg Ophthalmol Otolaryngol 1999;12:369–85.
109. Choi DY. Clinical study of effect of auricular acupuncture on stoping smoking. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 1996;13:202–11.
110. Lee JD, Choi DY, Park DS. Clinical research of the auricular acupuncture therapy on stop-smoking. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 1992;9:17–29.
111. Kim JD, Kwan CC, Lim NC. Clinical study of the effect of ear acupuncture on 233 alcoholics. J Kor Oriental Med Soc 1992;13:124–50.
112. Lee JH, Kim YC, Woo HJ. Clinical study on 133 cases of temperance (quit-drinking) therapy. J Oriental Med 1998;3:59–69.
113. Park JH, Peun SH. Clinical study of auricular acupuncture and herbal medicine in the treatment of alcoholism. J East-West Med 1996;21:1–15.
114. Lee SR, Lee KG. A clinical research of abdominal obesity by the electric acupuncture therapy. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 1996;17:336–44.
115. Jeong SH, Nam SS, Kim YS, Lee JD, Choi DY, Koh HK, et al. A clinical study on case of nine obesity patients by elecroacupuncture therapy. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 1999;16:39–56.
116. Lee ES, Kim YS. The effect of acupuncture treatment on weight regulation. J Oriental Rehabil Med 1996;6:365–77.
117. Kim YS, Kim CH, Kim KS. Effect of auricular acupuncture on postoperative nausea and vomiting. J Kor Acu Mox Soc 1996;17:331–6.
118. Kim KS, Kim DS, Shin KI, Kim YS. Effect of electric acupuncture stimulation of PC6 and PC7 antiemetic point on postoperative nausea and vomiting. J Kor Soc Anesth 1995;28:433–40.
119. Kim SW, Nam SS, Lee SK, Kim KS, Kim JK. The effects of electrostimulation on acupuncture loci upon duration of labor in primipara. Kyunghee Med 1999;15:198–202.
120. Kim JK, Kim SW. A clinical study on the effects of acupuncture anesthesia upon 31 cases of curettage. Kyunghee Med 1992;8:276–85.
121. Hwang WJ, Yang GB. The study on the effects of moxibustion on peripheral blood circulation. J Kor Oriental Med Soc 1997;18:499–505.
122. Ahn YM, Ahn SY, Doo HK. The change of temperature of external genitalia at the patients with impotence by using penile DITI. Kyunghee Med 1998;14:79–88.
123. You WK, Lee MJ, Oh JG. The effects of auricular acupuncture for obesity on the change of hormone and energy metabolism during weight control of veteran taekwondo players. J Oriental Rehabil Med 2000;10: 133–45.