Summary of Herbs that Are Used for Respiratory Symptoms
By Daniel Cho, L.Ac. (email: c0454445@gmail.com)
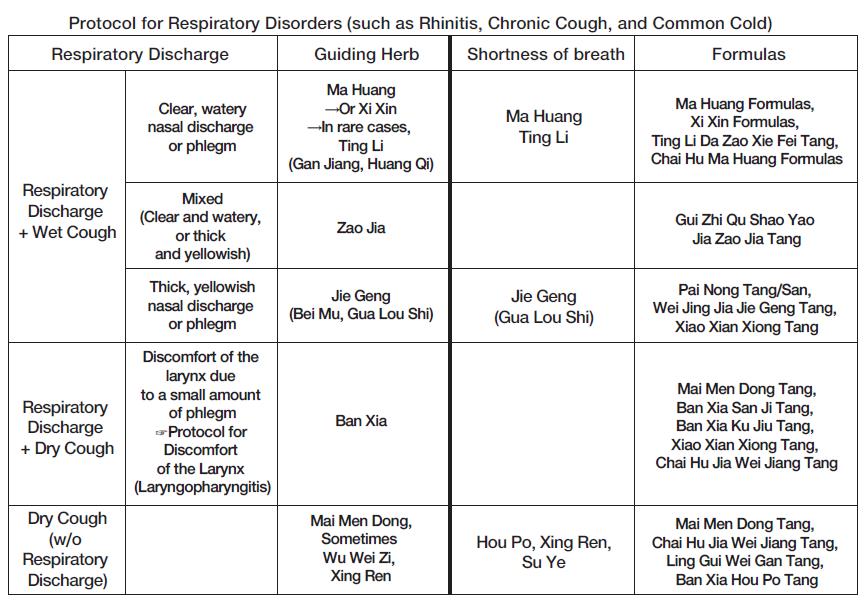
This month, we will study the herbs that could be used as a monarch herb in formulas for various respiratory symptoms. By understanding which herbs address specific symptoms patients report, selecting formulas from Shanghan Lun will become much more manageable.
Jie Geng
Symptom Indicator Score ++,
Frequency of Use++
Main Symptoms: Thick, yellowish respiratory discharge (nasal discharge, phlegm, dry snot) + coughing, nasal congestion, wheezing, shortness of breath.
Possible Symptoms: Throat discomfort, irritation, soreness, pain due to the main symptoms.
Another Main Symptom is redness, heat, swelling, pus and other symptoms due to purulent inflammation of the skin or internal organs.
Zao Jia
Symptom Indicator Score+
Frequency of Use+
Main Symptoms: Rhinitis with nasal obstruction is its primary symptom, or sometimes it is caused by a small amount of clear, watery nasal discharge. Gui Zhi Qu Shao Yao Jia Zao Jia Tang is used, and sometimes (rarely) Zao Jia Wan.
TIP: After ruling out Ma Huang, Xi Xin, Ting Li, and Jie Geng, you can consider Zao Jia.
Mai Men Dong
Symptom Indicator Score+ +
Frequency of Use++
Main Symptoms (In Mai Men Dong Tang and Zhu Ye Shi Gao Tang) Dry cough + dryness of the lips, mouth, throat, and sometimes hoarse voice.
Wu Wei Zi
Symptom Indicator Score+
Frequency of Use++
Main Symptoms: Dry cough (w/o nasal discharge or phlegm) ☞ Wu Wei Zhi is usually used with Ma Huang and Xi Xin, and in such cases, Wu Wei Zhi’s symptoms of dry cough (w/o nasal discharge or phlegm) are obscured.
Possible Symptoms: Heavy-headedness and dizziness (vertigo).
Xing Ren
Symptom Indicator Score+
Frequency of Use++
Main Symptoms: cough, shortness of breath (w/o nasal discharge and phlegm) ☞ Xing Ren is usually used with Ma Huang and Xi Xin. In such cases, Xing Ren’s symptoms of cough and shortness of breath (w/o nasal discharge and phlegm) become obscured.
Possible symptoms: chest fullness, pain, mild edema, constipation (due to lack of intestinal fluid).