Winston Lee L. Ac, Ph.D, KMD
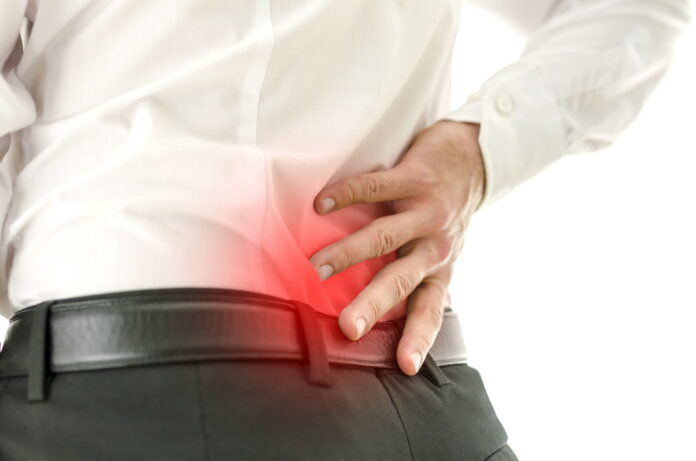
Mr. Leonard who is in his late 50’s suffers from severe pain on his lower back and leg. His pain started recently. Just after 30 minutes’ walk, he started feeling aching pain and tingling sensation on his right leg. And his pain relievers as soon as he sits down and rests. He cannot stand straightly. He described the kind of pain he had as heaviness, soreness and stiffness. At night the pain waked him up frequently.
Spinal stenosis is common in over 50’s like Mr. Leonard and should be examined carefully by doctors. Generally, patient’s average age of spinal stenosis is older than that of disc herniation. Most of the patients have vertebral degeneration. Because of these reasons, it’s not easy to treat spinal stenosis than disc herniation. Not to mention, the length of treatment is longer than disc herniation. When a patient neglects this problem without having any treatment, it would get worse for sure. Therefore, when it comes out, he or she must see a well-experienced physician immediately and should take some treatments on a regular basis for a long time.
Let me explain the difference between spinal stenosis and disc herniation. Symptoms from spinal stenosis and disc herniation are similar and it makes harder to distinguish. So, treatment plan should be made after precise and objective diagnosis.
First, spinal canal is like a pipe which starts from bottom of occipital bone and ends at sacrum bone at pelvic area. It is surrounded by vertebral bone and spinal cord is running through it. This canal might be narrowed by degenerated and thickened ligaments such as posterior longitudinal ligament or ligamentum flavum. This abnormal tissue of ligament is compressing the spinal cord or nerve and consequently it results in pain and tingling at hips and legs. This is the ‘spinal stenosis’. Low back pain could be accompanied by the radiating pain on legs but not always.
Disc herniation is different. Patient with herniation feels more pain when he or she bends down. On the contrary, spinal stenosis patient feels pain when the spine is straight or bended backward. Disc herniation patient feels better when the patient lay down on bed, but any activity or movement increases the pain. On the other hand, stenosis patient feels pain when he tries to stand up from laying down position. Pain usually will be reduced after walking.
Then how can we treat this spinal stenosis? First, acupuncture is very effective to control the radiating pain than any other method. The spinal stenosis patient’s sciatic nerve is compressed and pinched by abnormal tissue as described above. Along the sciatic nerve, most of muscle in low back, pelvis and legs are tightened and shortened. We can relieve the muscle spasm in the piriformis and gluteus medius muscle. Fortunately, acupuncture has been recognized as the only method to treat the spasm without any injury to other supportive tissue.
Simultaneously, herbal medicine should be prescribed to the patient. If we prescribe the medicine upon eastern diagnosis, it can be very effective toward this spinal stenosis. The pain is coming from inflammation at spinal cord aggravated by abnormal contact with other tissue such as thickened ligaments. The herbal medicine will decrease the inflammation in the spinal cord. This medicine will make a synergetic effect with acupuncture to control the pain in acute phase. Also, this medicine will strengthen the posterior longitudinal ligament and ligamentum flavum supporting vertebral bones and spinal cord. As you expect this effect can prevent its relapse in the future. In rare cases, a patient needs to undergo a surgery to remove severe bone spur made from long term degeneration. After the surgery, herbal medicine is capable to suppress the regeneration process and stimulates the recovery from scar tissue. Also, the medication will decrease chance to have side effects from a surgery.