The Dynamics of Shang Han Lun ⑫ Particulars-Part 1
By Jubong Kang, K.M.D.
Herbs: Chaihu (柴胡)
Ex. Formula: Shao Caihu Decoction (小柴胡湯)
Sentence
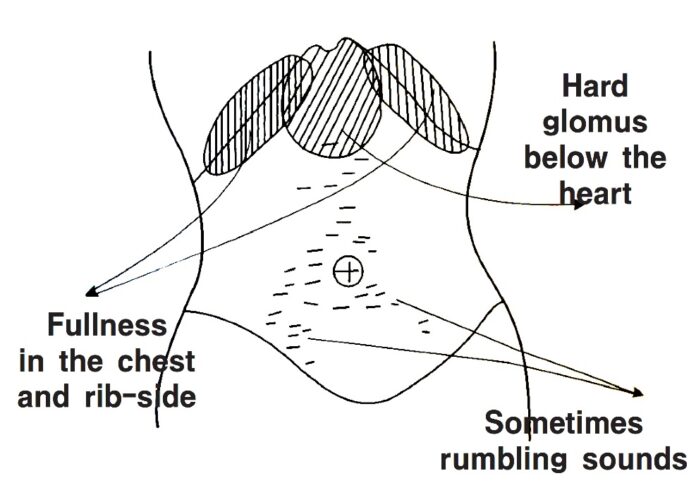
When cold damage that has lasted for five days, wind strikes, there is alternating aversion to cold and heat effusion, the person suffers from fullness in the chest and rib-side, taciturnity with no desire for food or drink, heart vexation and frequent retching, or possibly there is vexation in the chest and no retching, or thirst or pain in the abdomen, or hard glomus under the rib-side, or palpitations below the heart with inhibited urination, or absence of thirst wit mild generalized heat, or cough, ‘Shao Caihu Decoction’ governs. (ibid. Line 96, p.410, PPV)
Commentary (on ‘Guizhi Decoction’, ‘Gegen Decoction’ and ‘Shao Caihu Decoction’)
The reason for ‘fullness in the chest and rib-side’ can be interpreted by constitutional ‘organ theory’.
When the body is influenced by ‘cold damage’ there are three symptoms to this pattern of disease. And for these three symptoms, three basic formals are used in “Shang Han Lun”.
The first on is ‘Guizhi Decoction’, the second one is ‘Gegen Decoction’, and the third one is ‘Shao Caihu Decoction’.
First ‘Guizhi Decoction’ is useful for a person whose constitution belongs to ‘autumn type’ or ‘winter type’. This type of person has ‘smaller spleen’ and ‘bigger kidney’, so that the quantity of ‘liquid’ is smaller than that of other types.
In this type person was affected by ‘wind cold’, ‘liquid’ – the blood and the lymph – in the ‘middle burner’ would move to the superficial level to help ‘normal yang qi’ confront the ‘exterior evil factor’. Therefore, the digestive organs cannot hold enough ‘liquid’, because the quantities of liquid stored in the organs have become distributed unproportionately.
To treat this, ‘Guizhi’ in ‘Guizhi Decoction’ is used to warm the superficial level and attack ‘exterior evils’ to expel them and ‘Shaoyao’ in ‘Guizhi Decoction’ draws ‘liquid’ back into the superficial muscles and digestive organs with the extra liquid generated through support from ‘Gancao’.
The second case, ‘Gegen Decoction’ is available for a person whose respiratory organs are weak. The bronchi in the lungs are contracted from coldness, thus the ‘heart beating’ – heart rate – increase to warm up the lungs to expand the contracted bronchi.
To treat these ‘wind cold’ symtoms, ‘Shaoyao’ and ‘Gegen’ expand capillaries of the bronchi and neighbor muscles around the lungs to increase the volume of the blood flowing through neighboring vessels. And ‘Mahuang’ expands bronchi to cause more oxygen to be absorbed in the blood stream to produce more combustion to warm both the contracted bronchi and the box.
Furthermore, ‘Guizhi’ and ‘Mahuang’ promote ‘heart beating’ to increase the force of the heart pumping blood into capillaries of bronchi and superficial muscles to bring warmth and relaxation.
Above is an explanation of the functions of ‘Guizhi Decoction’ and ‘Gegen Decoction’, which become a foundation to interpret ‘sign symptom’ – ‘fullness in the chest and – rib side’ – of ‘Small Caihu Decoction’. In ‘four constitutions theory’, ‘Green Decoction’ can be used good results for all constitutional type.’
Commentary (2) On ‘Shao Caihu Decoction’
‘Fullness in the chest and rib-side’ presents in the ‘summer type person’ due to ‘four constitutions theory’. Even though the ‘spring type person’ also has a ‘bigger spleen’, his other organs are different from the ‘summer type person’. Therefore, the ‘spring type person’ has no relation to this sentence.
‘Guizhi Decoction’ is a formula for the ‘winter type person’ and the ‘autumn type person’, while for the ‘summer type person’, ‘shao Caihu Decoction’ si available. In 『Dong Yi Su Se Bo Won』, ‘Shao Caihu Decoction’ belongs to formulas for the ‘summer type person’.
The ‘summer type person’ has a bigger spleen and a small kidney, so that he has much more volume of ‘liquid’ in his body than other types, and has a smaller volume of urination: therefore, hos blood density is already thin.
If the ‘summer type person’ was affected by ‘wind cold’, then two kinds of patterns can occur, one is of ‘Gegen Decoction’, another is of ‘small Caihu Decoction’.
The pattern of ‘Gegen Decoction’ appears when the heart and the lungs are weak and vulnerable due to stress or overwork, and the weekend ‘heart beating’ cannot push enough blood to the lungs as written in the above interpretation.
When ‘heart beating’ is not weak and the liquid in the lung is not in want, the blood in the liver mobilizes to the region of the throat instead of into the bronchi.
And it’s necessary to understand that the state of mobilized blood from the liver to the vessels is not thin but condensed.
The region of the throat is governed not only by the lungs but also by the gallbladder through ‘shao yang gallbladder channel.’
When ‘wind cold’ attacks and provokes the region of the throat, if ‘gallbladder channel’ or ‘the gallbladder’ is overstimulated, but the ‘heart beating’ is not weak, then the condensed blood from the liver will not move into bronchi of the lung but into the ‘gallbladder channel.’ The lymph liquid is now drawn into gallbladder channel.’ Then this reaction creates ‘fullness in the chest and rib-side’ in the region of ‘gallbladder channel(『Huang Han Yi Xue(皇漢醫學)』, in the second volume, p52)’.
If both gallbladder channel and heart beating are weak, then a pattern emerges that unifies one of two decoctions – ‘Gegen Decoction’ and ‘Minor Caihu Decoction’ appears, the the combined formula is called ‘Cai Ge Jie Ji Decoction(柴葛解肌湯)’
A ‘Bigger spleen’ of the ‘summer type’ sends much more lymph liquid to the region of ‘gallbladder channel’ around the throat including the chest where the condensed blood was coming from the liver. This lymph liquid can dilute the condensed blood to increase immunity of tonsils and tissues of inner throat.