Shaoqinglong-Tang Also Treat Similar Symptom. Differential Diagnosis Is Required
By Kang, Ju Bong KMD
In celebration of 5th year of printing the newspaper, Kang, Ju Bong KMD decided to share his most updated clinical experiences with herbal formulas. Dr. Kang is the most renowned acupuncturist and lecturer among Korean acupuncturists in Korea. His lectures regarding the Sang Han Lun have been recognized as the most wanted lectures for years.
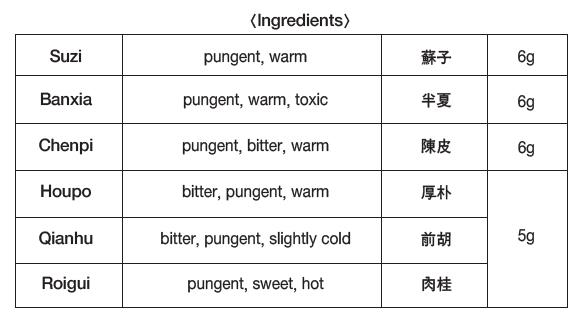
Analyzation Of The Formula: Among the constituent drugs, Suzi, as a monarch drug, dissolves stagnant-qi and eliminates phlegm with its pungent and warm property. And it lowers adversely rising-qi in the chest as descending character’s seeds to stop coughing and subside asthma. Banxia, Houpo, and Qianhu serve as ministers drugs. Banxia eliminates and dries phlegm, Houpo sends down dampness and phlegm, and Qianhu descends the adversely rising-qi and resolves phlegm. These three drugs take the role of stopping coughing and asthma. Danggui and Rougui are adjuvant drugs; the former supplements and activates blood, and the latter warms channels, expels coldness, and promotes blood circulation. Gancao has sweet properties, mediates other drugs to prevent distraction, and enriches the qi to bear as an adjuvant and guiding drug.
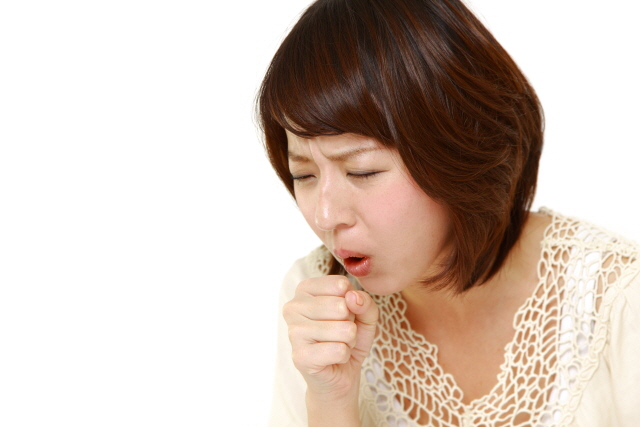
Actions and Diagnosis: This prescription treats various diseases such as cough, asthma, shortness of breath, dyspnea, tinnitus, vertigo, nosebleed, hemoptysis, limb edema, and in most cases, symptoms of foot coldness and scant urination caused by lung-qi’s failure due to stagnation of phlegm-retention in the chest area. The symptom is caused by a weakening of the lower body due to the collection of the qi and blood at the upper part to dispel the phlegm in the lungs.
Understanding How The Formula Was Formed: This prescription is combined with Banxia-Houpo-Tang, Shaocaihu-Tang, and Danggui-Jianzhong-Tang. In Banxia-Houpo-Tang, Suye was replaced by Suzi, and Qianhu replaced Caihu of Shaocaihu-Tang. in Danggui-Jianzhong-Tang, Shaoyao was removed, and Rougui was used instead of Guizhi. Banxia-Houpo-Tang releases qi-stagnation, dampness-phlegm, and retaining food in the upper and middle energizer to regulate qi and resolve phlegm and dampness. Danggui-Jianzhong-Tang treats exterior wind-cold causing headache, muscle pain, and joint pain by harmonizing ying-qi and wei-qi and supplementing and activating the blood. Shaocaihu-Tang treats half-superficies and half-interior symptoms in the throat, chest, and hypochondrium. In this way, Suzi-Jiangqi-Tang dispels wind-cold and damp-phlegm of Taiyang and Shaoyang’s evil factors spread in the upper and middle energizers and restores sthenia in the upper part and asthenia in the lower, and allows the qi and blood to exert a mechanism to rise and fall normally.
Suye was changed to Suzi in Banxia-Houpo-Tang because there are few superficies-syndrome and many adversely rising-qi symptoms. The reason that Shaoyao was removed from Danggui-Jianzhong-Tang is that no abdominal pain and sweat were not presented. The change of Caihu from Shaocaihu-Tang to Qianhu is mainly intended to eliminate phlegm and keep the adverse-qi downwards because there is no alternating fever or fever symptom. Suzi-Jiangqi-Tang does not contain diaphoretics that dissolve exterior pathogenic factors because the superficial symptoms are almost extinguished, and those of phlegm or dampness remain in the chest.
How To Modify The Formula: Suppose cough, asthma, or dyspnea are more severe at night. In that case, it is because of yin deficiency. Therefore, Maimendong-Tang should be combined. If the lower abdomen’s subsidence is remarkable and digestion is not weak, an appropriate amount of Shudihuang needs to be added. When abdominal palpitation is detected by the palpating, then add Fuling with Shudihuang. If the cun-kou pulse is weak, and the symptoms of qi deficiency, insomnia, or depression come out, Huangqi should be added.
Clues To Use The Formula: The pulse is often floating and gentle but sometimes weak or sunken. If the pulse is powerful, this prescription is not appropriate. If the pulse is sunken and severely weak, Huangqi should be added. And if the foot cold is severe, Ganjiang or Fuzi can be added according to the sign-symptoms.
Indications And Applications: Chronic cough, asthma, tinnitus, chronic bronchitis, hemoptysis caused by chronic bronchitis, pneumothorax, emphysema, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Differential Diagnosis And Distinction: Compare this with Shaoqinglong-Tang, which shows a lot of watery runny nose or cough due to the retaining water in the stomach, whereas Suzi-Jiangqi-Tang’s cough has a runny nose or phlegm, but it is not as watery or not a lot as the former.
<Ingredients>