A suggested treatment for the symptom
By Namwook Cho, L.Ac.
Many Americans have diabetes and suffer from the symptom directly and indirectly. Also, as acupuncturists, we have been dealing with diabetic-related symptoms daily in our clinic. Two different reasons cause type 2 diabetes. The pancreas does not produce enough insulin; cells respond abnormally to insulin and take in less sugar.
It is required to have different treatment approaches for the symptoms: pre-diabetes and Type 2 diabetes. And it is required to take care of different treatment strategies. Most studies showed that the Eastern medicinal treatment with herbs and acupuncture proved its efficacy in lowering glucose levels.
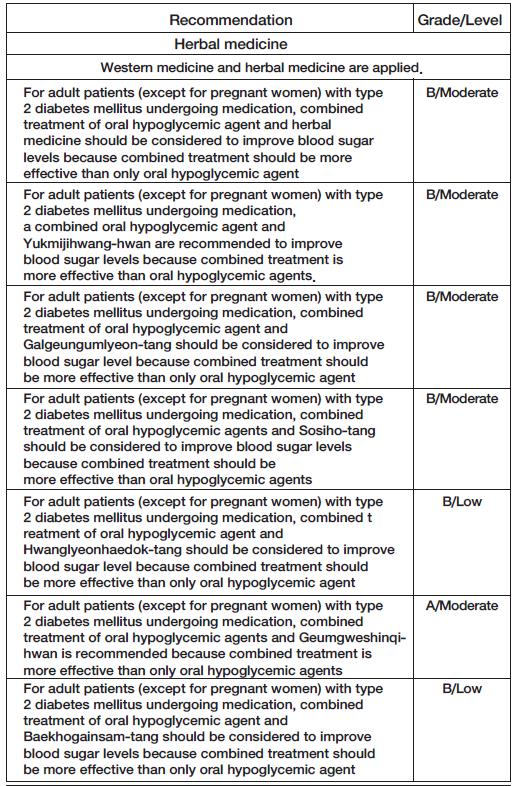
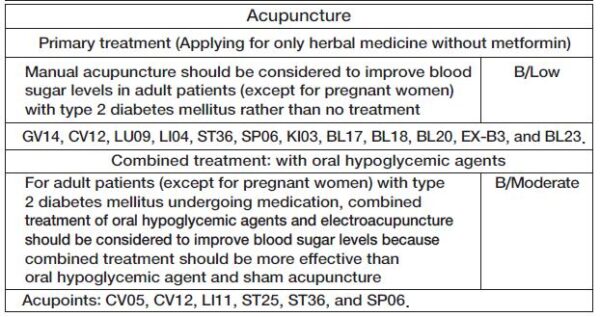
The recommendations are for applying herbal medicine to pre-diabetic and diabetic patients with or without a doctor’s prescribed medication.
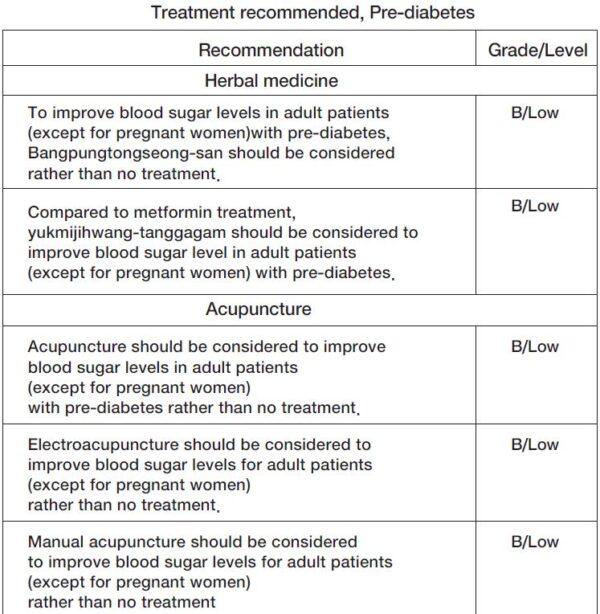
Pre-diabetes (ICD-10 code: R73.0) is a high-risk group with a high possibility of progressing to diabetes and is largely classified into impaired glucose tolerance and fasting glucose.
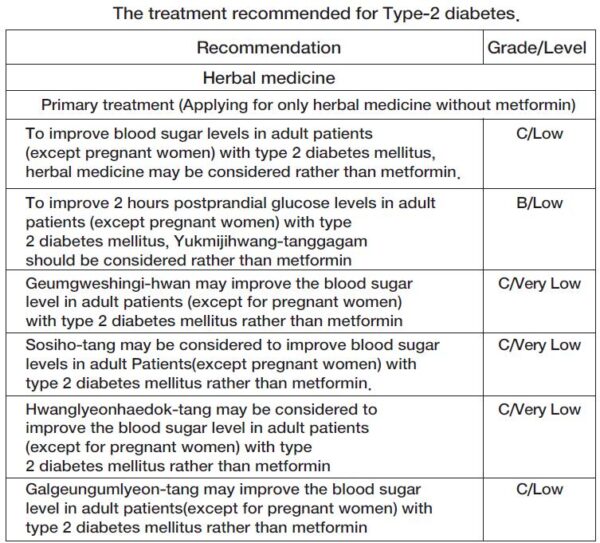
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (ICD-10 code; E10.9, E11.9, E12.9, E13.9, E14.9) is a chronic state of hyperglycemia caused by decreased insulin secretion or insulin tolerance. Occasionally, it does not show any specific clinical symptoms. But, when blood sugar rises rapidly, polydipsia, polyuria, and weight loss may occur, and sometimes fatigue and decreased visual loss may appear.
Suppose the clinical symptoms of diabetes are clear. In that case, it is similar to a ‘sogal(消渴)’ disease which is used to be called diabetes in Eastern medicinal terminology.
Diagnosis criteria for Pre-diabetes
It is defined as glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) of 5.7~6.4%.
- Impaired fasting glucose (IFG) is defined as 100 to 125mg/dL of glucose in fasting patients.
- Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) is defined as two-hour glucose levels of 140 to 199mg/dL on the 75-g oral glucose tolerance test.
Diagnosis criteria for type 2 diabetes
- Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c)≥6.5%.
- Fasting (over 8 hours) plasma glucose level≥126mg/dL.
- Plasma glucose≥200mg/dL 2 hours after a 75g oral glucose load as in a glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
- Random plasma glucose≥200mg/dL accompanied by clinical symptoms (polydipsia, polyuria, unexplained weight loss etc.).