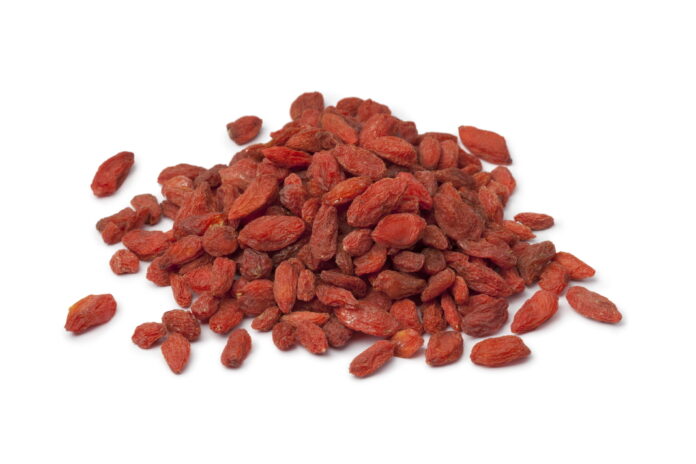
Goji Berry Has Been Used To Enhance The Respiratory Function By Adding Qi To Kidney and Liver
By Dae Sun Hong, L.Ac.
Goji Berry is also known as wolfberry in western culture and is a strong antioxidant and benefits degenerative eyes-related symptoms such as senile disciform macular degeneration and eye dryness due to prolonged usage time of computers, cell phones, or watching TV monitors. In Asian medicine, Goji berries have an indication for nourishing and tonifying the liver and kidney, strengthening eyesight, and nourishing the lungs.
Characteristics and Psychology of Goji berries
Goji berries benefit all organs but especially help on kidneys and liver. Symptoms such as dizziness, blurry vision, eye dryness, weakness in the lower back and knees with various pain, and ganacratia could be treated by Goji berries.
According to the article, “Goji Berry Effects on Macular Characteristics and Plasma Antioxidant Levels,” Goji Berry can benefit age-related macular degeneration: AMD, published in National Institutes of Health, NIH. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of daily supplementation with a proprietary milk-based formulation of Goji Berry, Lacto-Wolfberry (LWB), on macular characteristics, plasma zeaxanthin, and antioxidant capacity levels in elderly subjects. Overall, daily dietary supplementation with Goji Berry for 90 days increases plasma zeaxanthin and antioxidant levels as well as protects from hypopigmentation and soft drusen accumulation in the macula of elderly subjects. Zeaxanthin is one of only two carotenoids found in human eyes. It protects the eyes from the harmful effects of oxidation and light-induced damage, such as blue light from cellphones or notebook monitors. Research suggests that it may help delay or prevent the progression of eye diseases such as cataracts and age-related macular degeneration (AMD), the leading causes of visual impairment and acquired blindness in the United States, by preventing drusen which Drusen are deposited under the retina.
A proper diet with Goji Berry could control blood pressure and glucose level.
Benefits
Goji Berry reduces stress levels and relieves depressional feelings and anxiety. The berry also contains plenty of antioxidants. It could be used for eye-related symptoms such as senile disciform macular degeneration and protecting damage from blue light from cellphones, laptops, or TV monitors. Especially, Goji Berry and wild chrysanthemum tea help prevent dry eyes or amblyopia. Wild chrysanthemum cools down unnecessary heat from the body; therefore, the flowers have been used during summer to maintain health in Eastern countries.
Goji Berry could also be used with Bilberry. The combination helps those who drive long distances and prevents night blindness. It is also possible to use Lutein and Zeaxanthin supplements with Goji Berry to increase the absorption rate. I want to recommend taking the supplement with meals.
Other benefits of the berry are: losing weight, increasing the quality of night sleeping, lowering glucose levels, the antiaging process of the skin, increasing motor ability, protecting the liver from alcohol, and inhibiting fat deposit.
How to Take
Goji berries could be added to cereals and salads. Salads with Goji berries are especially beneficial for diabetes patients and hyperglycemia patients. Recommended daily amount of consumption is 15~20g.
Goji Berry is considered safe for taking long periods. But it could lower the glucose level of a patient on medication and unexpectively decrease blood sugar level. For this case, frequent glucose level checking is highly recommended. Rarely, Goji Berry could cause digestion-related symptoms such as indigestion and diarrhea among those with weak digestion function. To prevent the advert reaction of the berry, always start with a small dose for patients with frequently digestion-related symptoms.